Difference between revisions of "Hierarchical layout"
From BioUML platform
Tagir Valeev (Talk | contribs) |
m |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
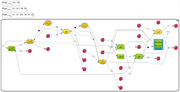
The hierarchical layout algorithm tries to arrange the compounds in a fashion that the irreversible reactions point in one direction. This type of visuallization is especially useful for metabolic pathways, in which the reactions occur only in one direction. The algorithm partitions the compounds into layers and than arranges the compounds in the layers, such that the number of crossings between different reactions is low. The hierarchic layout algorithm usually produces few crossings and no overlaps. However, if the data is not directed, the resulting layout may be not satisfactory and a [[Force directed layout|force-directed layout]] may be more appropiate. | The hierarchical layout algorithm tries to arrange the compounds in a fashion that the irreversible reactions point in one direction. This type of visuallization is especially useful for metabolic pathways, in which the reactions occur only in one direction. The algorithm partitions the compounds into layers and than arranges the compounds in the layers, such that the number of crossings between different reactions is low. The hierarchic layout algorithm usually produces few crossings and no overlaps. However, if the data is not directed, the resulting layout may be not satisfactory and a [[Force directed layout|force-directed layout]] may be more appropiate. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==See also== | ||
| + | * [[Diagram_document]] | ||
Revision as of 17:17, 14 June 2013
- Title
- Hierarchical layout
- Class
HierarchicLayouter
| This page or section is a stub. Please add more information here! |
The hierarchical layout algorithm tries to arrange the compounds in a fashion that the irreversible reactions point in one direction. This type of visuallization is especially useful for metabolic pathways, in which the reactions occur only in one direction. The algorithm partitions the compounds into layers and than arranges the compounds in the layers, such that the number of crossings between different reactions is low. The hierarchic layout algorithm usually produces few crossings and no overlaps. However, if the data is not directed, the resulting layout may be not satisfactory and a force-directed layout may be more appropiate.